7 Ways DeFi Can Increase Trading Volume and Liquidity for Tokenized Financial Assets
Leveraging AMMs, Lending Protocols, and Stablecoins to Unlock the Potential of RWAs
Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency and blockchain, revolutionizing the way we think about digital value and transactions. It introduced atomic transaction execution with near-instantaneous finality, solving challenges like Delivery vs Payment (DvP) settlement.
The next wave of innovation came with smart contracts, first introduced by Ethereum in 2013. These programmable and composable contracts transformed blockchains into platforms for Decentralized Finance (DeFi) — enabling a new generation of financial applications. DeFi protocols leverage the immutability and transparency of smart contracts to offer services like trading, lending, and automated asset management, redefining the future of finance.
This blog post explores the applications of tokenized financial assets (real-world assets - RWAs) in DeFi, how they can be integrated into protocols like Aave or Uniswap, and why proper calibration is necessary to manage risks and maximize efficiency.
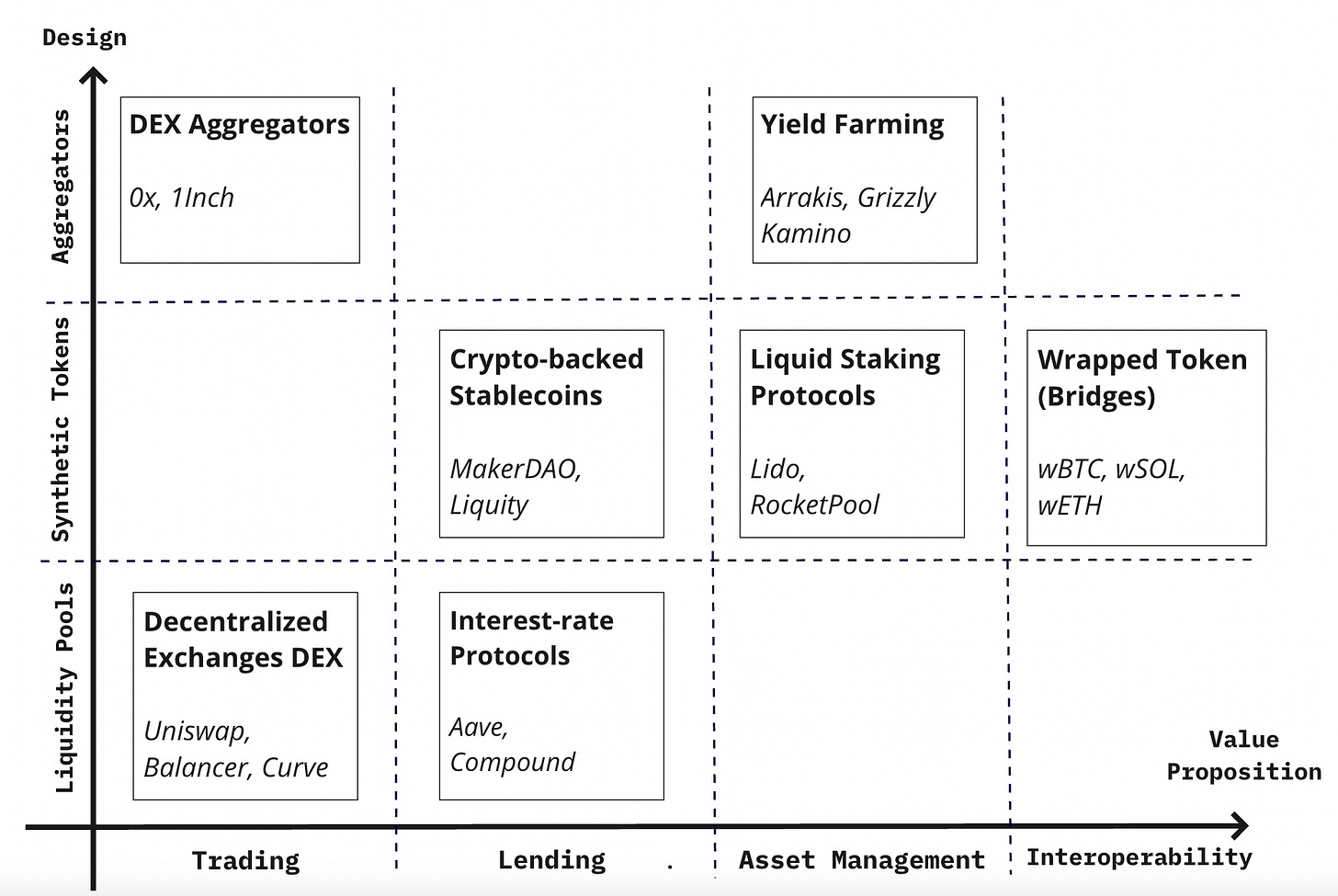
7 Use Cases of Tokenized Financial Assets in DeFi
Here are 7 ways DeFi can increase trading volumes and liquidity for tokenized RWAs:
1. Listing on Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
RWAs can be listed on AMMs like Uniswap or Curve. If compliance requirements are met, they can be traded freely and 24/7. AMMs provide a decentralized alternative to traditional exchanges, ensuring liquidity and access to diverse assets.
2. Collateral for DeFi Lending
RWAs can serve as collateral on lending platforms such as Aave, Morpho, or Compound. This allows users to borrow stablecoins or other crypto assets by locking their tokenized RWAs as collateral.
3. Leveraging RWAs
By combining Use Cases 1 and 2, users can leverage their RWAs. For instance, RWAs can be deposited as collateral, loans can be taken against them, and the borrowed funds can be reinvested, creating a leveraged position.
4. Mortgage-Like Flash Loans
DeFi introduces innovative applications like using flash loans to purchase tokenized RWAs. Even without sufficient liquidity upfront, users can acquire RWAs through a one-block atomic transaction, similar to a mortgage in traditional finance.
5. Liquidity Provision (LP) on AMMs
Tokenized RWAs can be deposited into AMM liquidity pools, earning trading fees. However, LPs should be cautious of impermanent loss and arbitrage risks, especially with coupon payments that can be captured by arbitrageurs if miscalibrated.
6. LPs for Lending Protocols
RWAs can also be used to provide liquidity to lending protocols. LPs earn interest by supplying assets to the protocol, which borrowers use. Proper calibration of loan-to-value (LTV) ratios and liquidation thresholds is critical to minimize risks.
7. Stablecoin Minting
Tokenized RWAs can be used to mint stablecoins by locking them as collateral. This enables the creation of new liquidity with minimal interest costs, as the system effectively secures the stablecoin against RWAs.
Key Considerations for Integration into DeFi
AMMs and Tokenized RWAs
Selecting the right AMM design is essential. For example:
Curve v1 or Uniswap v3 are ideal for two stablecoins pegged to the same asset.
Tokenized bonds require AMMs that support a dirty price model, as most DeFi AMMs are incompatible with rebase tokens.
Misaligned AMM configurations can result in inefficiencies and arbitrage losses.
DeFi Lending Protocols
DeFi lending differs from traditional systems by being pool-based, overcollateralized, and operating without KYC requirements.
Risk calibration in DeFi lending depends on price trajectories of borrowed assets, ensuring adequate liquidation thresholds and loan-to-value ratios.
Blockchain Selection
Should you choose a permissioned or permissionless blockchain? Public or private? Layer-1 or Layer-2? Selecting the ideal blockchain for your tokenized assets and DeFi protocols is becoming increasingly complex. However, with thorough due diligence that properly evaluates both technical and business considerations, you can make the right decision.
A critical requirement for any DeFi use case is ensuring the blockchain can execute DeFi smart contracts. This capability is predominantly found in ecosystems like Ethereum or Solana, which have established themselves as leaders in DeFi.
5 Reasons why Deutsche Bank went for Layer-2 Blockchain
Just before the Christmas break, Deutsche Bank, a leading European financial institution, announced the launch of its new blockchain initiative, leveraging a layer-2 blockchain solution. While many banks, such as JP Morgan, have experimented with blockchain technology, Deutsche Bank's announcement stands out because it marks the bank's first foray into …
From Central Banks to DeFi: BIS and MAS Pilots
DeFi protocols inspired by central bank projects like Project Mariana and Project Guardian demonstrate the potential of tokenized RWAs:
Cross-Border Repo: Tokenized government bonds traded using smart contracts enable atomic transactions with reduced settlement risks.
FX Exchange: Using RWAs in cross-border FX exchanges improves efficiency and settlement times.
These projects highlight how DeFi's programmability can redefine traditional markets, and pilots run by the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) with central banks are paving the way.
8 Predictions on TradFi and DeFi Convergence from the Roundtable Discussion at the University of Basel
I recently had the privilege of participating in a roundtable discussion on decentralized finance (DeFi), organized by the University of Basel and led by Professor Fabian Schär and his team [link]. This event was a unique gathering of representatives from leading traditional finance (TradFi) institutions, including the Swiss National Bank (SNB), UBS, th…
Conclusion
Tokenized financial assets represent a bridge between traditional finance and DeFi, unlocking new possibilities in trading, lending, and liquidity management. However, the success of integrating RWAs into DeFi depends on proper calibration of parameters like LTV ratios, liquidation thresholds, and AMM designs. Projects like Mariana and Guardian showcase the transformative potential of tokenization for financial markets.
Next Steps: If your institution is interested in piloting the application of tokenized financial instruments—such as stablecoins, tokenized deposits, tokenized bonds, or other digital assets in DeFi—let’s connect.
Reach out to discuss how we can collaborate to bring these innovative solutions to life!






